[Inside Vue] 4. Initialize - _init 함수

이번 포스트에서는 Vue 코어 함수에서 호출하는 _init 함수의 초기화 동작에 대해 이야기 할 것입니다.
_init 함수 살펴보기
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}위의 코드는 코드 함수 코어 입니다. 이번 포스트에서는 this._init 함수를 살펴 보도록 하겠습니다.
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})Vue를 사용할 때, 위의 코드처럼 Vue 인스턴스를 생성합니다. 위의 코드와 같이 Vue 인스턴스를 생성하는 것은
options = {
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})위의 코드와 같은 값을 가진 options로 this._init(options)를 호출 한다는 것과 동일합니다.
_init 함수는 이전 포스트. 3. Initialize - Mixin Layer에서 살펴본 src/core/instance/init.js 파일에 initMixin 함수 안에 있습니다.
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
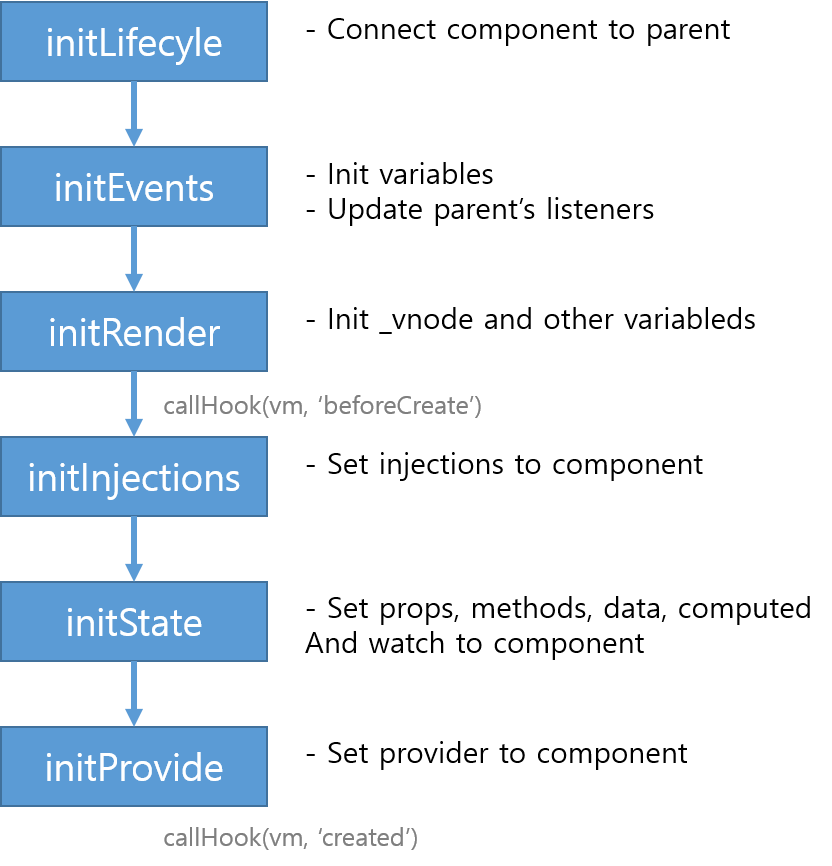
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}_init 함수가 하는 일들은
_uid값을 세팅합니다.- 퍼포먼스 확인을 위한
startTag가 mark 됩니다. _isVue값을 세팅합니다.- option들을 세팅합니다.
_renderProxy를 세팅합니다. Proxy는 개발모드일 때 랜더 정보를 보여줍니다._self를 세팅합니다.- init 함수들을 호출합니다.
- 퍼포먼스 확인을 위한
endTag가 mark 됩니다. $mount함수가 호출되어 DOM을 업데이트 합니다.
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')위의 init 함수들에 대해 이야기 하도록 하겠습니다. callHook 함수는 간단하게 Vue의 lifecycle 훅을 호출하는 함수로 이해 할 수 있습니다.
initLifecycle 함수
initLifecycle 함수는 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js에 정의되어 있습니다.
export function initLifecycle (vm: Component) {
const options = vm.$options
// locate first non-abstract parent
let parent = options.parent
if (parent && !options.abstract) {
while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {
parent = parent.$parent
}
parent.$children.push(vm)
}
vm.$parent = parent
vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm
vm.$children = []
vm.$refs = {}
vm._watcher = null
vm._inactive = null
vm._directInactive = false
vm._isMounted = false
vm._isDestroyed = false
vm._isBeingDestroyed = false
}initLifecycle 함수는 현재 컴포넌트를 부모와 연결 시키는 역할을 합니다. 그리고 lifecycle 메소드에 필요한 몇몇 변수들을 초기화 합니다.
initEvents 함수
initEvents 함수는 src/core/instance/events.js에 정의되어 있습니다.
export function initEvents (vm: Component) {
vm._events = Object.create(null)
vm._hasHookEvent = false
// init parent attached events
const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners
if (listeners) {
updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners)
}
}initEvents 함수는 몇몇의 변수들을 초기화 하고, 부모의 리스너를 초기화 합니다.
initRender 함수
initRender 함수는 src/core/instance/render.js에 정의되어 있습니다.
export function initRender (vm: Component) {
vm._vnode = null // the root of the child tree
vm._staticTrees = null // v-once cached trees
const options = vm.$options
const parentVnode = vm.$vnode = options._parentVnode // the placeholder node in parent tree
const renderContext = parentVnode && parentVnode.context
vm.$slots = resolveSlots(options._renderChildren, renderContext)
vm.$scopedSlots = emptyObject
// bind the createElement fn to this instance
// so that we get proper render context inside it.
// args order: tag, data, children, normalizationType, alwaysNormalize
// internal version is used by render functions compiled from templates
vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false)
// normalization is always applied for the public version, used in
// user-written render functions.
vm.$createElement = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, true)
// $attrs & $listeners are exposed for easier HOC creation.
// they need to be reactive so that HOCs using them are always updated
const parentData = parentVnode && parentVnode.data
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
defineReactive(vm, '$attrs', parentData && parentData.attrs || emptyObject, () => {
!isUpdatingChildComponent && warn(`$attrs is readonly.`, vm)
}, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$listeners', options._parentListeners || emptyObject, () => {
!isUpdatingChildComponent && warn(`$listeners is readonly.`, vm)
}, true)
} else {
defineReactive(vm, '$attrs', parentData && parentData.attrs || emptyObject, null, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$listeners', options._parentListeners || emptyObject, null, true)
}
}_vnode와 _staticTrees를 초기화 합니다
Vue를 사용하면서 VNode라는 말을 들어 보셨을 수도 있습니다. VNode를 사용하여 VDom을 만듭니다. VNode와 VDom은 각각 real Node와 DOM에 매칭됩니다. Vue가 VNode와 VDom을 사용하는 이유는 가상 DOM을 사용하여 성능을 향상 시키기 위해서 입니다.
initInjections 함수
initInjections 함수는 src/core/instance/inject.js에 정의되어 있습니다.
export function initInjections (vm: Component) {
const result = resolveInject(vm.$options.inject, vm)
if (result) {
toggleObserving(false)
Object.keys(result).forEach(key => {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
defineReactive(vm, key, result[key], () => {
warn(
`Avoid mutating an injected value directly since the changes will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the provided component re-renders. ` +
`injection being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
})
} else {
defineReactive(vm, key, result[key])
}
})
toggleObserving(true)
}
}initInjections 함수는 짧고 간단합니다. 이 함수는 option 삽입 문제를 해결하고, 삽입된 option들을 컴포넌트에 세팅합니다. initInjections 함수에 defineReactive 함수가 사용된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
defineReactive 함수
Vue는 data가 변경 되면 자동으로 view를 업데이트 합니다. 이 업데이트 동작이 defineReactive 함수와 연관되어 있습니다. defineReactive 함수는 이곳 저곳에서 많이 사용됩니다.
defineReactive 함수는 src/core/observer/index.js안에 정의되어 있습니다.
/**
* Define a reactive property on an Object.
*/
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep()
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) return
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}첫줄에는 const dep = new Dep()가 정의되어 있고, 유효성 체크과, getter와 setter의 추출하는 코드를 확인 할 수 있습니다. 그 다음에는 let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)가 정의 되어 있고, get과 set으로 감싸는 코드가 나옵니다.
data가 변경되어 view를 업데이트 해야 할 때, getter와 setter 안에서 이 data와 의존성(dependency)이 있는 것들에게 notify 합니다. defineReactive는 5. Reactive - Observer, Dep and Watcher에서 더 자세히 이야기 하도록 하겠습니다.
initState 함수
initState 함수는 src/core/instance/state.js에 정의되어 있습니다.
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}initState 함수에서는 Vue을 사용하면서 많이 접하게 되는 props, methods, data, computed, watch들이 이 함수에서 등장합니다.
initProps 함수
function initProps (vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {
const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}
const props = vm._props = {}
// cache prop keys so that future props updates can iterate using Array
// instead of dynamic object key enumeration.
const keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []
const isRoot = !vm.$parent
// root instance props should be converted
if (!isRoot) {
toggleObserving(false)
}
for (const key in propsOptions) {
keys.push(key)
const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm)
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
const hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key)
if (isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) ||
config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) {
warn(
`"${hyphenatedKey}" is a reserved attribute and cannot be used as component prop.`,
vm
)
}
defineReactive(props, key, value, () => {
if (!isRoot && !isUpdatingChildComponent) {
warn(
`Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. ` +
`Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's ` +
`value. Prop being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
}
})
} else {
defineReactive(props, key, value)
}
// static props are already proxied on the component's prototype
// during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy props defined at
// instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key)
}
}
toggleObserving(true)
}유효성 검사와, defineReactive를 사용하여 props를 get과 set으로 감싸 컴포넌트에 세팅하는 역할을 합니다.
initMethods 함수
function initMethods (vm: Component, methods: Object) {
const props = vm.$options.props
for (const key in methods) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (typeof methods[key] !== 'function') {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has type "${typeof methods[key]}" in the component definition. ` +
`Did you reference the function correctly?`,
vm
)
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a prop.`,
vm
)
}
if ((key in vm) && isReserved(key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" conflicts with an existing Vue instance method. ` +
`Avoid defining component methods that start with _ or $.`
)
}
}
vm[key] = typeof methods[key] !== 'function' ? noop : bind(methods[key], vm)
}
}컴포넌트에 methods를 세팅하는 역할을 합니다.
initData 함수
function initData (vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {}
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
)
}
// proxy data on instance
const keys = Object.keys(data)
const props = vm.$options.props
const methods = vm.$options.methods
let i = keys.length
while (i--) {
const key = keys[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property.`,
vm
)
}
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. ` +
`Use prop default value instead.`,
vm
)
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
}
}
// observe data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}유효성 검사와 proxy 함수를 이용하여 data 세팅을 합니다. proxy 함수는 initProps에서도 등장합니다.
export function proxy (target: Object, sourceKey: string, key: string) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter () {
return this[sourceKey][key]
}
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter (val) {
this[sourceKey][key] = val
}
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)
}위의 코드는 proxy 함수입니다. 간단히 살펴 보면 this.name을 this_data['name']으로 매핑하는 작업을 하는 함수 입니다.
initData 함수는 마지막으로 observe(data, true /* asRootData */)를 호출합니다. Observe는 5. Reactive - Observer, Dep and Watcher에서 더 자세히 이야기 할 것이지만, 간단히 살펴 보면,
/**
* Attempt to create an observer instance for a value,
* returns the new observer if successfully observed,
* or the existing observer if the value already has one.
*/
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value)
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}observe 함수는 value에 대한 observe 인스턴스를 리턴하는 함수 입니다. 두 번째 파라미터에 true를 전달하면 root data로 사용한다는 의미이고, ob.vmCount는 얼마나 많은 컴포넌트가 해당 value를 root data로 사용하는지 카운팅 하는 역할을 합니다.
initComputed 함수
function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) {
// $flow-disable-line
const watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)
// computed properties are just getters during SSR
const isSSR = isServerRendering()
for (const key in computed) {
const userDef = computed[key]
const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && getter == null) {
warn(
`Getter is missing for computed property "${key}".`,
vm
)
}
if (!isSSR) {
// create internal watcher for the computed property.
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions
)
}
// component-defined computed properties are already defined on the
// component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined
// at instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
defineComputed(vm, key, userDef)
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (key in vm.$data) {
warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined in data.`, vm)
} else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) {
warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined as a prop.`, vm)
}
}
}
}전달 받은 두번째 파라미터인 computed의 getter 속성을 추출합니다. 추출된 getter는 Watcher 인스턴스를 만드는데 사용하고, 생성된 Watcher 인스턴스는 watchers 배열에 저장됩니다.
defineComputed 함수를 사용하여 컴포넌트에 computed 속성을 세팅합니다.
initWatch 함수
function initWatch (vm: Component, watch: Object) {
for (const key in watch) {
const handler = watch[key]
if (Array.isArray(handler)) {
for (let i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i])
}
} else {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler)
}
}
}전달 받은 두번째 파라미터인 watch의 내부 각각의 값에 createWatcher를 사용하여 watcher를 생성합니다.
function createWatcher (
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
handler: any,
options?: Object
) {
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
options = handler
handler = handler.handler
}
if (typeof handler === 'string') {
handler = vm[handler]
}
return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)
}위의 코드는 createWatcher 함수입니다. createWatcher 함수는 vm.$watch를 호출합니다. $watch는 3. Initialize - Mixin Layer에서 살펴본 stateMixin 함수 안에서 정의 됩니다.
initProvide 함수
initProvide 함수는 src/core/instance/inject.js에 정의되어 있습니다.
export function initProvide (vm: Component) {
const provide = vm.$options.provide
if (provide) {
vm._provided = typeof provide === 'function'
? provide.call(vm)
: provide
}
}initProvide 함수는 option 안에 provide를 추출하고 호출하는 역할을 합니다.
요약
다음으로 볼 것
다음 포스트에서는 data가 변경 되면 화면이 동기적으로 업데이트 되는 방법, 5. Reactive - Observer, Dep and Watcher에 대해 이야기 할 것입니다.